Achilles Tendonitis: What Athletes Should Know

If you enjoy running, jumping, or any sport that keeps you on your feet, you rely heavily on your Achilles tendon, the thick band of tissue that connects your calf muscles to your heel bone. It’s what propels you forward when you sprint, helps you push off the ground when you jump, and absorbs the shock with every landing. But when that tendon is overworked or strained, you may find yourself dealing with Achilles tendonitis, a common yet troublesome injury among athletes and active individuals.
Left untreated, this condition can cause lingering pain and affect your ability to move comfortably. If you’ve been experiencing stiffness or soreness near your heel, it could be time to consult an Achilles tendonitis specialist in Singapore. Keep reading to learn more about this condition, and the steps you can take to support recovery.
What Is Achilles Tendonitis?
The Achilles tendon is the body’s largest and strongest tendon, linking the calf muscles (gastrocnemius and soleus) to the heel bone (calcaneus). Despite its resilience, it’s vulnerable to injury, particularly from repetitive motions or sudden changes in activity levels.
Achilles tendonitis develops when this tendon becomes inflamed or irritated, often due to microscopic tears that occur over time. Without timely management, the condition can progress to Achilles tendinopathy, where the tendon begins to degenerate and lose its strength.
Causes and Risk Factors
Achilles tendonitis often stems from a combination of overuse, poor training habits, and biomechanical issues. Common causes include:
- A sudden increase in training intensity or duration
- Inadequate stretching before or after exercise
- Flat feet or abnormal gait that overloads the tendon
- Tight calf muscles that reduce flexibility
- A history of previous tendon injuries
While athletes in sports like running, football, and basketball are particularly prone to this condition, it’s not limited to professionals. Many middle-aged individuals who suddenly return to vigorous activity after a break may also develop symptoms due to reduced tendon elasticity.
Symptoms of Achilles Tendonitis
Symptoms usually appear gradually, starting as mild discomfort that worsens with ongoing activity. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Pain or stiffness along the back of the heel, especially in the morning or after periods of rest
- Swelling or thickening of the tendon
- Pain that intensifies when walking, running, or climbing stairs
- Reduced ankle flexibility or tightness in the calf
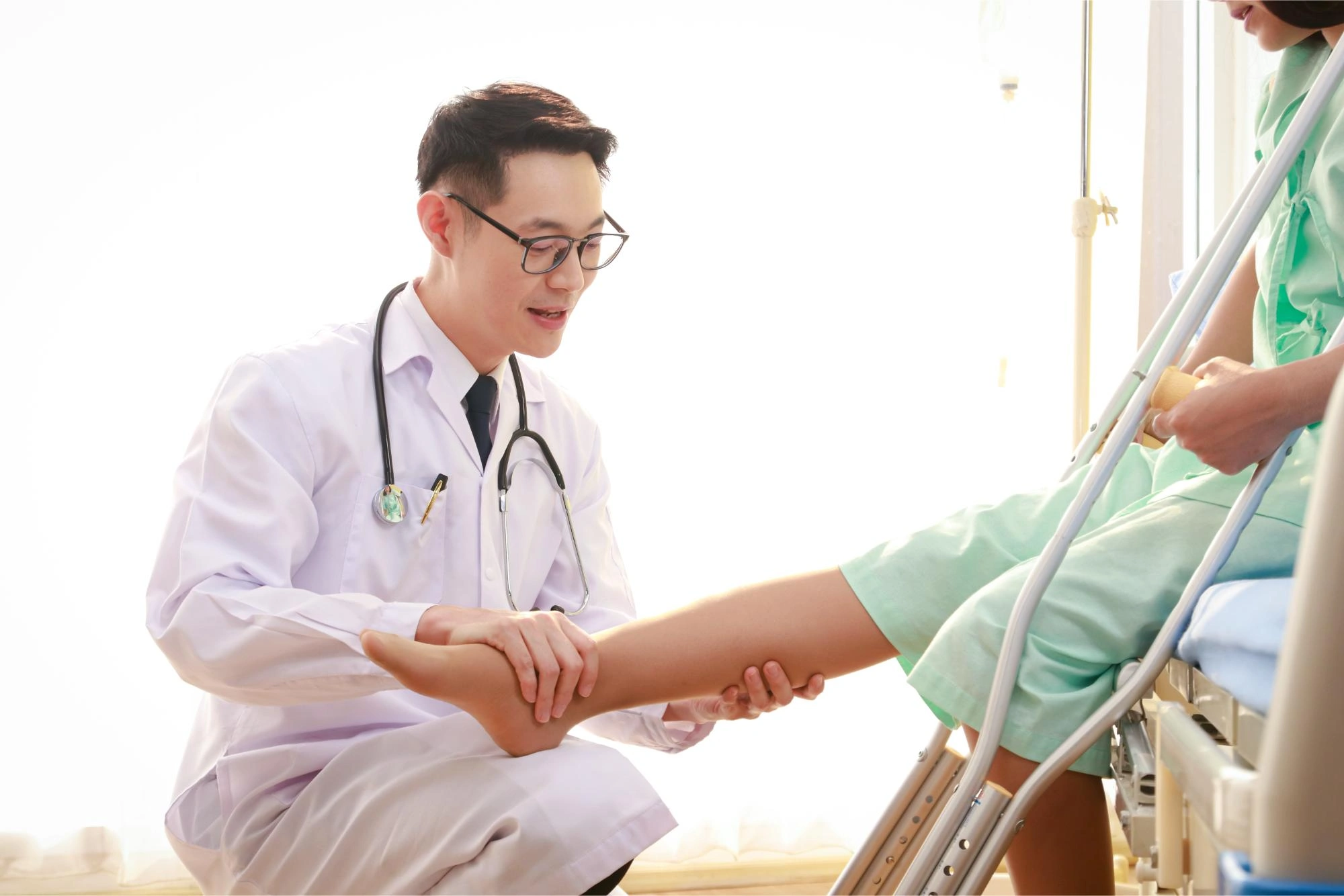

How Is Achilles Tendonitis Diagnosed?
When you visit an Achilles tendonitis doctor in Singapore, your consultation will typically begin with a thorough physical examination. The doctor will assess tenderness, swelling, and your ankle’s range of motion. They may also gently press along the tendon to check for thickening or stiffness.
To confirm the diagnosis and gauge its severity, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI scans are often recommended. These allow the doctor to visualise inflammation or degeneration within the tendon and distinguish between acute inflammation and chronic tendinopathy.
Achilles Tendonitis Treatment in Singapore
Most cases of Achilles tendonitis improve with conservative, non-surgical management focused on easing pain, restoring movement, and promoting tendon healing.
Treatment options include:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Reducing or avoiding high-impact movements allows the tendon to recover.
- Physiotherapy: A tailored programme of stretching and strengthening exercises can restore flexibility and support the healing process.
- Footwear Modification or Orthotics: Supportive shoes or heel lifts can lessen pressure on the tendon during movement.
- Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help ease discomfort and reduce inflammation.
- Shockwave Therapy: This method encourages tissue repair and can be useful for chronic cases.
If symptoms persist despite these measures, further evaluation at an Achilles tendonitis clinic may be necessary. For severe or long-standing cases involving partial tendon tears or degeneration, surgical repair may be recommended to restore proper function and prevent further complications.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
A structured rehabilitation approach plays a key role in regaining strength, flexibility, and overall ankle function. This typically involves several targeted strategies, including:
- Gradual Return to Physical Activity: Activities are reintroduced in stages to allow the tendon time to adapt and prevent overload.
- Strengthening Calf and Foot Muscles: Specific exercises rebuild muscle strength, support the tendon, and improve overall stability during movement.
- Improving Flexibility and Balance: Stretching and proprioception training enhance ankle mobility and stability, helping prevent further strain.
- Preventing Re-injury: Learning proper warm-up routines, training techniques, and using supportive footwear reduces the likelihood of future tendon problems.
Persistent heel or calf pain should not be ignored, as early medical attention can prevent the condition from worsening. With professional care from an Achilles tendonitis doctor, you can regain strength, restore mobility, and return to your regular activities safely and confidently. To schedule an appointment, contact us today.