Most Common Knee Injuries and What to Look Out For
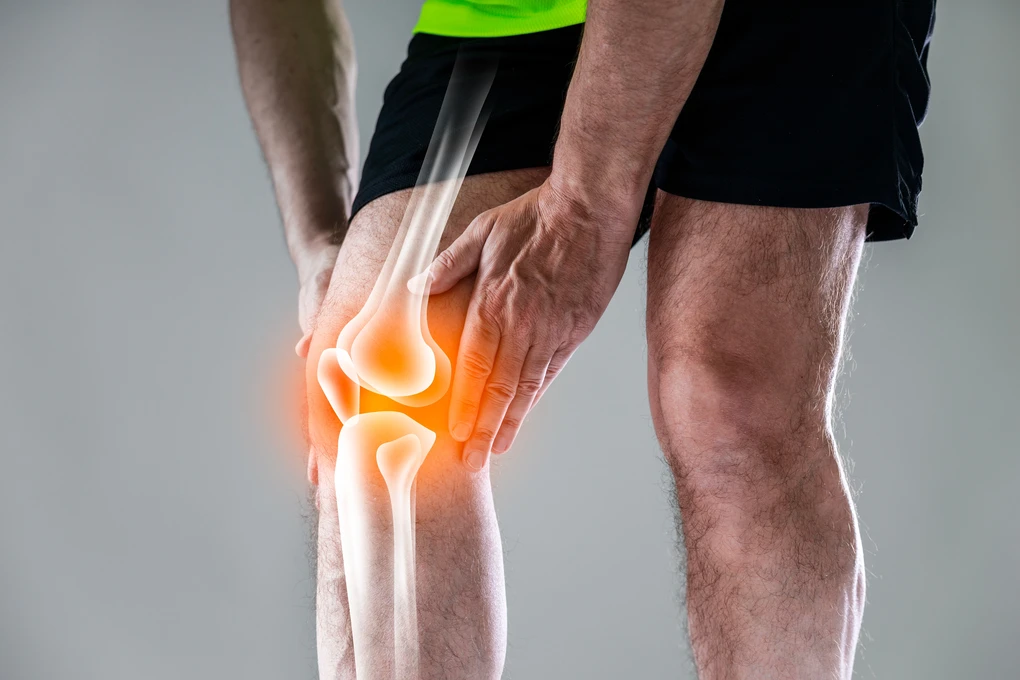
Understanding the most common types of knee injuries and their symptoms can help you identify problems early and seek the appropriate care. In this article, we explore the most frequent knee injuries seen in orthopaedic practice and what signs you should be aware of.
What it is:
The ACL is one of the key ligaments that helps stabilise your knee joint. It connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia). ACL injuries often occur during sports that involve sudden stops, jumps, or changes in direction, such as football, basketball, or skiing.
What to look out for:
- A popping sound or sensation at the time of injury
- Rapid swelling
- Severe pain and inability to continue activity
- Instability or "giving way" when bearing weight
Treatment:
Depending on the severity, treatment can range from physiotherapy and bracing to surgical reconstruction, especially in athletes or active individuals.
What it is:
The meniscus is a piece of cartilage that acts as a cushion between your femur and tibia. Meniscus tears are often caused by twisting motions while bearing weight, commonly occurring during sports or due to age-related degeneration.
What to look out for:
- A popping sensation
- Pain, particularly when twisting or rotating the knee
- Swelling and stiffness
- Difficulty straightening the knee fully
Treatment:
Minor tears may heal with rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), and physiotherapy. Severe or persistent tears might require arthroscopic surgery to repair or remove the damaged part.
Patellar Tendinitis (Jumper's Knee)
What it is:
This condition involves inflammation of the patellar tendon, which connects the kneecap (patella) to the shin bone. It’s common in athletes who frequently jump, such as volleyball or basketball players.
What to look out for:
- Pain just below the kneecap
- Swelling and tenderness in the area
- Pain that worsens with activity or after exercise
- Weakness in the knee
Treatment:
Early-stage treatment includes rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medications, and strengthening exercises. In chronic cases, more advanced interventions such as shockwave therapy or injections may be required.
Knee Bursitis
What it is:
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint. Inflammation of these sacs, known as bursitis, can result from repetitive kneeling, overuse, or trauma.
What to look out for:
- Swelling over the kneecap or on the inner side of the knee
- Warmth and tenderness
- Pain when moving or pressing on the area
Treatment:
Most cases can be treated with rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medication. Severe or persistent bursitis may require aspiration or corticosteroid injections.
Knee Fractures
What it is:
Fractures can occur in any of the bones that make up the knee joint, most commonly the patella. These are usually caused by high-impact trauma, such as falls or car accidents.
What to look out for:
- Intense pain and swelling
- Inability to straighten or bear weight on the knee
- Obvious deformity in some cases
Treatment:
Treatment varies based on the location and severity of the fracture. It may involve immobilisation with a brace or cast, or surgical intervention to realign and stabilise the bones.
Dislocated Knee or Patella
What it is:
A dislocation occurs when the bones of the knee are forced out of alignment. Patellar dislocation is when the kneecap slips out of place, usually to the outside of the knee.
What to look out for:
- Visible deformity or displacement
- Intense pain and swelling
- Inability to move the knee
Treatment:
Immediate medical attention is required to relocate the joint. Rehabilitation and bracing are usually necessary afterward, and in some cases, surgery may be considered.
When Should You See a Specialist?
Knee pain that persists beyond a few days, especially when accompanied by swelling, instability, or difficulty
moving the joint, should be evaluated by an orthopaedic specialist. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent
further damage and help you return to your normal activities sooner.
At Axis Orthopaedic Centre, we offer comprehensive diagnostic and treatment services for a wide range of knee
injuries. Whether you’re recovering from a sports injury or managing chronic joint pain, our team is here to
support you every step of the way.
If you're experiencing knee discomfort or have concerns about a recent injury, don’t hesitate to reach out and
schedule a consultation with our experienced orthopaedic specialist.